Completed Research
D.S.T. Project
| Title of Project | Authors | Presented At |
|---|---|---|
| D.S.T. Project |
Dr. V.G.Vaidya Dr. U.G.Naik Mr. Sharad Gante |
Ministry of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, New Delhi. |
Summary & Conclusion :
Action Oriented Pilot Research study aimed at developing a model strategy to provide Occupational Health Service to industrial population employed mainly in unorganised small units and living scattered in slums who from economically and socially weaker sections of the society.
Trades Covered
Brick, Stonecurshing, Construction & Transport.
Workers examined : 2526
Unit covered: 85
Free Treatment Given to workers: 960
Findings :
Since unorganised small units are not covered under any legislation and are deprived of health services, it is advisable to provide general health services by voluntary organisations in surroundings small units and integrate occupational health services in phased manner, depending upon priority.
Recommendations :
Government should consider health and occupational services on priority basis
Development of low cost strategies and its utility.
- Provision of medical health care at the place of working through ambulatory care units.
- Integration of general health services with occupational health services
- Participation of Vol. Agencies, large scale industries and small unit organisation in providing package of medical care.
- State and Central Government should give 1/3 financial assistance for voluntary agencies doing this work.
Health Education
Development of low cost protective aids
Development and Training of Workers in unorganised units for early diagnosis and on the spot first aid treatment.
Following in depth studies should be undertaken :
Study of migration characteristics of working population in unorganised small units with reference to epidemical determinants and distribution. Development of strategies of integration of voluntary agencies and inputs from large scale industries and Government financial assistance. A detailed study is required to identify the nature of child labour exploitation in unorganised small units. Basic education should be made a vital aspect of health programme.
Study of acute Chlorine Gas Inhalation
| Title of Project | Authors | Presented At |
|---|---|---|
| Study of acute Chlorine Gas Inhalation |
Dr. V.G.Vaidya Dr. S.M.K.Hussainy Dr. U.G.Naik |
All India I.A.O.H(1981) |
Summary & Conclusion :
Seventy six workers from a paper and pulp factory admitted to Lokmanya Foundation’s Hospital for acute chlorine inhalation were studied. They were exposed to chlorine gas in separate incidences. Many has repeated exposures.
The usual symptoms were dry cough, irritation of nose and pharynx, chest pain and giddiness. The symptoms lasted for 10 minutes to 96 hours. All patients were followed up to one month. All patients showed complete recovery. There was no evidence of damage detected in the chest X-ray.
Inspection of factory showed that 80 percent of the accidents could be avoided by use of gas mask in cylinder connection and pulp testing operations.
This is preliminary communication of an occupational health research scheme undertaking by LOKMANYA MEDICAL FOUNDATION HOSPITAL to study effect of Industrial exposures to irritant gases.
Early Detection of Cancer
| Title of Project | Authors | Granted By |
|---|---|---|
|
Early Detection of Cancer Project Duration (Oct.1992 to March 1994) & (April 1995 to March 1996) |
Dr. V.G.Vaidya Dr. B.G.Sahasrabudhe Mr. Sharad Gatne Dr. D.S.Kelkar Dr. J.A.Jogi Dr. Rajashree Mitkar Mr.S.B.Pattar Mr.B.S.Sawant |
Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Govt. of India. |
Summary & Conclusion :
In pursuance of the Government of India's National Cancer Control priorities, early detection activity, was implemented through Cancer Detection Camps.
Completed Research
| Registration of Patients | History Recording |
| Primary Screening | Examination by Specialists |
| Special Investigations | Advice & Counselling |
Follow - up :
Referral systems has been established from camp to the base hospital. Each patient is given a referral card & is advised to attend specialist O.P.D. as required for investigation and treatment.
Basic Statistics of Detection Camps :
| Number of Rural Camps Organised | 109 |
| Number of Urban Camps Organised | 23 |
| Number of Patients referred to the Cancer - Specialists | 7904 |
| Number of path Investigations made like PAP Smears, Biopsies, X-Rays etc. | 521 |
| Number of Positive Cases Detected | 58 |
| Patients treated free | 91 |
This activity is found to be very useful to the Community on following counts
- It educates them regarding signs & symptoms of the disease & increases their awareness regarding early detection of cancer.
- It educated the on the ill-effects of addictions like tobacco chewing & smoking & ill conceived diets.
- It motivates them to come forward to attend the camps & reap the benefits of early detection.
Encouraging spacing methods & sterilisations
| Title of Project | Authors | Granted By |
|---|---|---|
|
Early Detection of Cancer Project Duration (Oct.1992 to March 1994) & (April 1995 to March 1996) |
Dr. V.G.Vaidya Dr. B.G.Sahasrabudhe Mr. Sharad Gatne Dr. D.S.Kelkar Dr. J.A.Jogi Dr. Rajashree Mitkar Mr.S.B.Pattar Mr.B.S.Sawant |
Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Govt. of India. |
Summary & Conclusion :
In pursuance of the Government of India's National Cancer Control priorities, early detection activity, was implemented through Cancer Detection Camps.
Completed Research
| Registration of Patients | History Recording |
| Primary Screening | Examination by Specialists |
| Special Investigations | Advice & Counselling |
Follow - up :
Referral systems has been established from camp to the base hospital. Each patient is given a referral card & is advised to attend specialist O.P.D. as required for investigation and treatment.
Basic Statistics of Detection Camps :
| Number of Rural Camps Organised | 109 |
| Number of Urban Camps Organised | 23 |
| Number of Patients referred to the Cancer - Specialists | 7904 |
| Number of path Investigations made like PAP Smears, Biopsies, X-Rays etc. | 521 |
| Number of Positive Cases Detected | 58 |
| Patients treated free | 91 |
This activity is found to be very useful to the Community on following counts
- It educates them regarding signs & symptoms of the disease & increases their awareness regarding early detection of cancer.
- It educated the on the ill-effects of addictions like tobacco chewing & smoking & ill conceived diets.
- It motivates them to come forward to attend the camps & reap the benefits of early detection.
Industrial Hand Injuries
| Title of Project | Authors | Presented At |
|---|---|---|
| Retrospective analysis into Aetiology of Industrial Hand Injuries |
Dr. V.G.Vaidya Dr. U.G.Naik |
10th Asian Conference on Occupational Health, Singapore. |
Summary & Conclusion :
542 cases of hand injuries reporting to Lokmanya Hospital & Research Centre during May 1981 to November 1981 were studied with a view to find out the aetiology of the accidents & the role of personal protective devices in the prevention of these injuries.
The following observations were made :
- Major share of hand injuries (80.07%) were observed in major/minor engineering industries.
- Of the other 11 categories of workers, helpers, fitters and turners were affected most frequently.
- Maximum cases (81.37%) belonged to the age group of 20 to 35 years.
- Maximum accidents were in workers with an experience of 1 to 4 years.
- Lack of proper pre employment technical training was found to be a significant aetiological factor.
- Analysis of accidents sequence revealed that 97.79% of accidents were preventable by correcting unsafe actions and unsafe conditions.
- Analysis of injuries showed that 75.09% were of minor nature. The reason for apparently low incidence were discussed. Left hand was affected significantly more often in certain categories of jobs.
- It was found that 69.93% of injuries occurred because of failure of workers to use personal protective devices.
It was concluded that 97.79% of lost time accidents which resulted in hand injury could be effectively prevented by :
- Ensuring safe environment conditions at work place.
- Insisting on proper pre-employment training including safety education.
- Proper guidance & supervision.
- Provision of properly designed gloves & ensuring their proper utilisation by persuasive & educatory methods.
Impact of Two way Education on Hand Injuries
| Title of Project | Authors | Presented At |
|---|---|---|
| Impact of Two way Education on Hand Injuries |
Dr. V.G.Vaidya Dr. S.M.K.Hussainy Dr. U.G.Naik |
11th Asian Conference on Occupational Health, Singapore. |
Summary & Conclusion :
The vital importance of hand, the most needed appendage of human body, need not be emphasised, especially in the context or the workers in the industrial echelon, who use their hands as the most versatile and valuable tool. This is even more important in India where human labour still remains the most important resource.
Unfortunately hand remains the most commonly affected part in industrial accidents. Experience of many researchers as well as our own experience confirm that as many as 34 to 43% industrial accidents result in injury to hand.
A retrospective analysis of 590 cases of hand injuries treated by our hospital during December 1979 to February 1980 revealed many important pointers which prompted us to undertake detailed research into epidemiology, prevention, rehabilitation, socio-economic implications etc. of industrial hand injuries.
- Effects of Audio-Visual shows were followed regarding prevention of accidents.
- A.V session was conducted to 7543 subjects in various industrial establishments.
- Careful collection of history & other environmental factors studied in accident cases.
- Subjects were exposed to A.V show followed by followed by group discussion, distribution of pamphlets & leaflets.
- Group A comprised 15 industries with 2260 subjects, exposed once.
- Group B comprised 8 industries with 3990 subjects, exposed twice with a gap of 6 months.
- Group C comprised 1 industry of 750 workers, exposed to show 12 times at monthly interval.
- Group A & B shows transient decrease in accidental rates immediately after exposure with reversal of usual pattern of accidents.
- Group C shows persistent decrease in accidents throughout the year.
- A.V shows with monthly interval is advisable.
- Search for other epidemiological factors of accidents and ways to mitigate the still confine.
Health Profile of Workers in Aluminium Foundry
| Title of Project | Authors | Granted By |
|---|---|---|
| Health Profile of Industrial Workers in Aluminium Foundry |
Dr. V.G.Vaidya Dr. B.G.Sahasrabudhe Dr. D.S.Kanade Dr. J.A.Jogi |
Ministry of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, New Delhi. |
Summary & Conclusion :
Purpose of the Study
- To ascertain the status of the Foundry workers
- To find out the impact of working environment on health related problems
Method & Organisation of Health Check-Up
Purpose of the Study
- Four packages for workers were designed
- Health care package for small units having less than 20 employees.
- Pre-employment health check-up package
- Essential health check-up package
- Comprehensive health check-up package
Pre-Designed Questionnaire was recorded on the following points
Purpose of the Study
- Demographic Aspects
- Occupational History
- H/o exposure to chemical & physical agents
- Working conditions
- Investigations required - minimum
Health profile study of 81 Aluminium Foundry workers was done as a part of the health schemes developed for industrial workers. Overall nutrional status was found to be unsatisfactory. Exposure to physical agents in 24 workers with poor nutrional status should be viewed carefully in future to find out any disturbances in haemodynamic mechanism.
57 workers with tobacco chewing habits should be subjected to screening for oral cancer. Tobacco chewing has been proven to be a major risk factor for oral cancer. Incidence of oral cancer in all ethnic group ranges from 44% to 45% in different parts of the country. Thus the health related problems like anemia, tobacco chewing habit and underweight were discovered due to periodical health check-ups.
Among Aluminium smelters who are exposed to poly hydrocarbon, bladder cancer is known. Smoking was an additive effect there was no urinary complaints in 81 workers.
Feedback from the Management was quite satisfactory and cost effective because their working day was not affected. This health check-up scheme has also helped in preparing basic data related to physical examination of the workers. Subsequently, this may help in early diagnosis of work related problems and health status of the workers.
AIDS Awareness Programme
| Title of Project | Authors | Granted By |
|---|---|---|
| AIDS Awareness Programme among Industrial workers |
Dr. V.G.Vaidya Dr. B.G.Sahasrabudhe Dr. U.G.Naik |
N.A.C.O & Govt. of Maharashtra |
Summary & Conclusion :
| Number of Rural Camps Organised | 109 |
| I.E.C. material prepared for workshop & awareness | Booklet, Folders, Question Answer Booklet, Posters, Exhibition charts, Slide set |
Study Methods :
The beneficiaries of the AIDS exhibitions were interviewed by the trained volunteers and different information about their knowledge regarding AIDS were collected from them.
Findings
- 100% of the visitors were aware that AIDS is caused due to a virus & risk is more due to sexual intercourse with HIV infected partners.
- 94% of visitors have the knowledge of AIDS symptomology.
- 100% visitors knew that there is no treatment of AIDS and morality is certain.
- 93% visitors were of the opinion that sexual relations with the HIV infected partners should be avoided.
- There should be no issue and use of condom should be compulsory, 51% of the visitors said that condom gives part protection against AIDS.
- If need arises for taking any injection preferential use of disposable syringes and needles was reported by 98% visitors.
- 57.20% visitors were of the opinion that Blood Donation was responsible for the spread of AIDS.
- It was experienced that social belief acted as a stumbling block in case detection surveillance and control measures.
Environment exposure in the handling of explosive
| Title of Project | Authors | Granted By |
|---|---|---|
| "The Assessment of working environment exposure in the handling of explosive/ non explosive chemicals in the working environment "- In respect of I & NG". |
Dr. S.B. Ray, Dr. V.P Joshi, Dr. Manjushri Dutta Choudhary |
High-explosives materials Laboratories (Defence-R&D establishment) Pune |
Introduction :
The aim of this project was to assess from acute and chronic toxicity view point, the working environment in the handling of explosive/ non explosive chemicals with reference to two chemicals viz. Toluene 2,4- Diisocyanates (2,4 I) and Nitroglycerine (NG)
Objective :
- The assessment of the working environment
- To determine the concentration of chemicals viz. Toluene 2,4- Diisocyanates (2,4 I) and Nitroglycerine (NG), representing the exposure to the working personnel from the stand point of both chronic and acute toxicity, covering symptomatic part.
- To give recommendations based on the findings and adopted remedial measures.
Method :
Both the chemicals viz I and Nitroglycerine were estimated by HPLC Method. The estimation process comprises of three parts namely standard line preparation, air sample collection from the working environment and analysis.
I and Nitroglycerine in the work place was trapped with the help of air sampling pump at a flow rate of 2 L/min in a fritted bubbler / midget impinger tube containing 10 ml of 0.0002 molar nitro reagent in Toluene for I and 5 ml of Methanol for Nitroglycerine for varying periods depending on operation duration and sensitivity of HPLC analysis.Then after collecting the samples they were analysed by HPLC method to find out the concentration of I and Nitroglycerine in the working environment.
Result :
-
Working Environment Assessment for I exposure
- Permissible level of exposure as per American conference of Government Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) 2000
- Threshold Limit Value -Time weighted average (TLV-TWA) of I-0.005 ppm or 0.036 mg/m3 in air
- Threshold Limit Value -Short term exposure level/ceiling (TLV-STEL/Ceiling) of I -0.02 ppm or 0.14 mg / m3 in air
- It was found that the I concentration in the working environment in all types of operation -small, medium and large scale were mostly above short term exposure limit (STEL) value. However the work was not of continuous type, being carried out as per requirement only.
- Eye irritation has been found in most of the I exposed workers while throat irritation and head ache have been found in few others
-
Working Environment Assessment for NG exposure
- Permissible level of exposure as per American conference of Government Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) 2000
- Threshold Limit Value -Time Weighted Average (TLV-TWA) of nitroglycerine-0.05 ppm or 0.46 mg/m3
- The Nitroglycerine concentration in the working environment in the medium scale operation was within the TWA value (0.05 ppm), except in the case of mixing of casting liquid where it was significantly above TLV-TWA. Taking into consideration the frequency of operation, operation duration, exposure level may be considered to be within permissible limit.
- While headache has been the major symptom in the NG exposed workers, Nausea /Vomiting and dizziness has been found in some others.
Conclusions :
Both Toluene Diocyanate (2, 4) and Nitroglycerine (NG) have got acute and chronic toxicity
In 19 working spots of handling, the concentration was found mostly above the STEL value although the work was of intermittent nature.
However taking into consideration the exposure symptoms of td exposed workers, additional / meticulous continuation of the existing remedial measures have been suggested.
In case of NG handling, although the exposure level was mostly within the permissible level, taking into consideration the sporadic exposure symptoms meticulous continuation of the existing remedial measures have been suggested.
Study of Metals Concentration in Drinking Water
| Title of Project | Authors | Presented at |
|---|---|---|
| "Comparative Study of Metals Concentration in Drinking Water of Different Areas of Pune Municipal Corporation and Pimpri Chinchwad Municipal Corporation and its Possible Link to Cause Hypothyroidism" | Dr.S.B.Ray | Industrial Hygiene Laboratory, LMRC |
Summary Conclusion:
- Within acceptable limits, PCMC drinking water generally shows higher conc. in respect of Zn, Co, Mg & Fe.
- PMC drinking water shows higher conc. in respect of Ni, Cu, and Cd. Out of the metal Conc. of Cd is higher than permissible level. However, conc. of all metals except Cd on certain occasions has not exceeded the allowable limits. Mercury estimation was done by the cold vapour method on subsequent five occasion viz. June 98, Sep. 98, Dec. 98, Mar 99 & June 99 Hg Conc. on the first two occasions was found above the permissible level of 0.0001 ppm, & on the last three occasion the conc. was well within limit. Henc
- The conc. of Cd has been found to be generally (marginally) higher in both PMC & PCMC water. According to American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists TLV (2003) an exposure to Cd, elemental and compounds is a suspected human carcinogen.
Linking of metal conc. in drinking / river water with frequency of hypothyroidism will be spelt out in a research paper in future.
Assessment of hazard due to Lead exposure”
| Title of Project | Authors | Presented at |
|---|---|---|
| "The Assessment of Working Environment hazard due to Lead exposure" |
Dr. S.B. Ray, Dr. V.P Joshi, Ms. Purnima Joshi, Ms. Smita Saykar |
Honeywell |
Introduction :
Lead is a cumulative poison and exposure beyond the permissible level of 0.05 mg/m3 can lead to chronic/ acute toxicity of the exposed working personnel. Some of the symptoms of Lead poisoning include Anemia, Lead-line on the gums, high Lead levels in blood and urine, insomnia, hypertension, and gray facial color may also be noted. Female employees particularly in the reproductive age are more sensitive to lead exposure giving rise to infertility.
Objective :
- To monitor Lead content in the breathing zone of the operator.
- Assessment of Lead content in the working environment.
- To check up the symptomatic part of Lead exposure amongst the working population.
- To give recommendations to minimize lead exposure as required in the working environment.
Method :
For determining Lead in the working environment, the air samples near the breathing zone of the workers/operators were drawn by using air flow meter and sucked air was absorbed in 1:99 HNO3 in an impinger. After suitably reducing the volume of Nitric Acid media containing absorbed Lead, the Lead content was directly measured in an Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer. Workers exposed to Lead fumes were medically examined for general and Lead specific symptoms.
Result :
It was found that lead concentration in some of the sections (viz Rework Room and Wave Soldering Machine area) was above the threshold limit value (TLV-TWA)
Although TWA indicates average exposure, taking into consideration the high exposure level in the section as a whole, exposure can be considered higher than allowable limit.
In case of two female employees exposed to Lead fumes higher than the permissible level, symptoms like Hb /anemia and infertility were observed.
Conclusions :
- Introduction of Source Exhaust System as also improvement in the effectiveness of the general exhaust system.
- The workers were recommended to use personal protective equipment such as half face high efficiency particulate respirator, suitable for protection against Lead fumes /Lead dust.
Since women workers were more susceptible to lead fumes and dust, the women operators should not be employed in the areas where there was Lead exposure.
Role OfYogic Practices In The Management Of Patients With Chronic Backache Problems With Particular Refrence To Activity Related Efficiency (1999-2003)

A research project sanctioned by Indian system of homeopathic and medicine, Government of India, was undertaken by Lokmanya medical research centre titled “Role of Yogic Practices in the Management of Patients with chronic backache problems, with particular reference to activity related efficiency.”
With an Aim To investigate and study various etiological factors and Psychological determinants in patients with chronic backache problems who are conservatively and or surgically treated and to assess the impact of Yogic practices and approaches on activity related efficiency in work life situation.
Study Design & Methodology
950 patients were randomly selected and distributed equally pair into two groups of conservative treated group and surgically intervened group; this was further divided into two groups into study and control group. Yoga was advised to these patients.
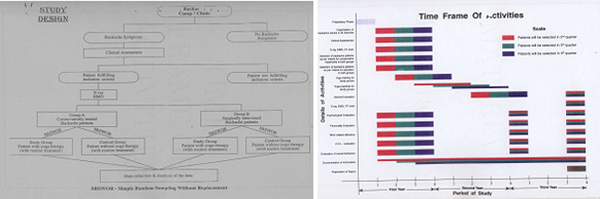
Study Abstract
This study demonstrated that the problem assumes greater significance with industrial workers being increasingly prone to spinal problems. Back pain is perhaps the most common medical condition that cuts across all age groups and the leading cause of reduced work related efficiency and increased absenteeism. The symptoms complex appears to be most prevalent in individuals during their prime productive period. In addition, it was seen that the sedentary workers had more back problems. About 86.04% patients were suffering from backache in between moderate to more severe pain The symptom appears to be increasing in frequency, despite our advancing knowledge of its pathogenesis and management. Like many research our study also proved that objective test (Viz radiological / Laboratory analysis) of back pain have limited value when it comes to final outcome of the treatment.

Patients who were given yoga showed better symptomatic pain relief (as compared to control group) and a good change toward positive side when their personality was assessed. Positive change was seen in personality factors viz. shift from emotionally unstable to stable, tensed to relaxed, group dependent to self
sufficient and undisciplined to controlled. Further the patients who were given yoga showed better work related efficiency and reduced absenteeism as compared to those not given yoga.
A significant change is observed in Comparison of year I & III findings in radiological assessment of patients, about 253 (56%) patients were totally relieved from backache due to yoga. Further while assessment of clinical improvement, 282 patients (63.51%) Excellent improvement is seen. Symptomatic relief has been more significant in patients given yoga therapy. Even the satisfaction level seems to be better in the patients who had yoga.127 (28.60%) patients show satisfactory improvement, indicating that 92.11% of patients have shown significant improvement.
41.67% patients show improvement in doing domestic activity, work related efficiency is improved in both groups, Sexual behavioral problem & absenteeism is reduced in Study group of conservatively & surgically treated groups.

This project also gave us a chance to highlight a need to establish yoga diagnosis to make yoga therapy to become complete in itself. Dr.Bhole’s approach of “Yoga Health Education and Practice (Abhyasa)” has become one of the important highlighting features of this project in this respect.
Yoga can be a very important tool in management of back pain and is effective in reducing pain scale, improving activity of daily life & work related efficiency.to reduce absenteeism and for improving work related efficiency.
